|
At present the best energy resolution for gamma-quanta
and electrons in high energy physics experiment is obtained with
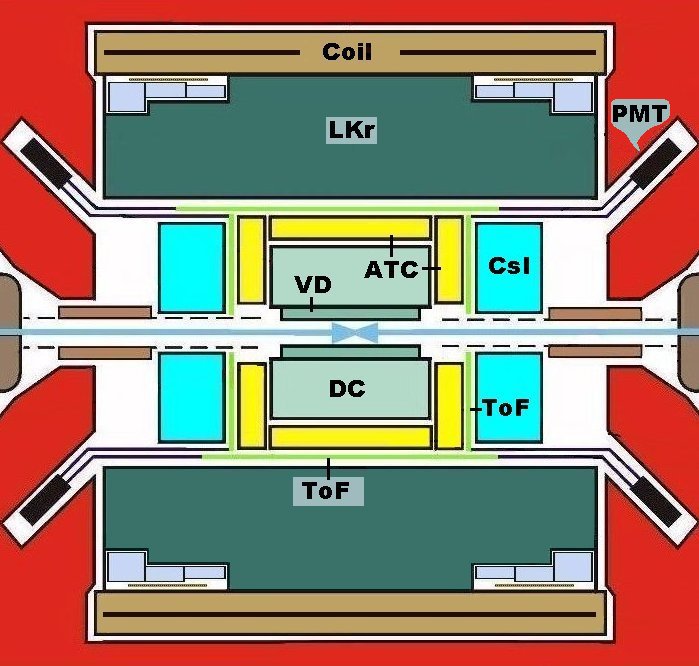
electromagnetic calorimeters based on scintillation crystals. In 4pi
detectors, to combine the high energy resolution for photons with
momentum
analysis for charged particles, the electromagnetic calorimeter is placed
inside a magnetic field. This excludes application of conventional PM
tubes.
The usual solution for the current large detectors is usage of Tl doped
CsI crystals with the light read out by silicon PIN diodes. At low
energies
the energy resolution of such calorimeter is dominated by the electronic
nose, the achieved level which is 150-200 keV of equivalent energy
deposition.
Another solution was proposed for an endcap calorimeter of the KEDR
detector where CsI crystals doped with Na viewed by vacuum phototriodes
are used.
|


![]()